Discover the advantages of green building materials! Uncover how they boost energy efficiency, save money, and promote healthier living. Start your green journey today!
Ever wondered about the advantages of green building materials? Well, you’re in the right place!
These eco-friendly heroes are more than just a trend. They’re transforming our world, making our buildings more sustainable, and creating healthier spaces for us to live and work in.
From boosting energy efficiency to saving us money, and even promoting healthier living, green building materials are truly changing the game.
So, let’s dive in and explore the use of sustainable materials together!
The Advantages of Green Building Materials
Welcome to our deep dive into the world of green building materials!
If you’ve ever been curious about how these sustainable alternatives can make a difference, you’re in for a treat.
In this post, we’ll explore the many advantages of green building materials, from their positive environmental impact to their surprising economic benefits.
We’ll also delve into how they contribute to healthier communities and more efficient use of natural resources.
Plus, we’ll answer some frequently asked questions and even touch on the leading green building standards.
So, buckle up and get ready for an enlightening journey into the future of green construction!
Introduction to Green Building Materials
Let’s start our journey by getting to know what green building materials are all about.
Picture this: you’re building a house, but instead of traditional bricks and cement, you’re using materials that are kinder to our planet. That’s the essence of green building materials.
They’re all about constructing in a way that reduces the environmental footprint, without compromising on quality or aesthetics.
Definition of Green Building Materials
So, what exactly are green building materials?
Well, they’re materials that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building’s life cycle.
This means from planning to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and even demolition, these materials are the stars of the show.
They could be made from recycled products, like reclaimed wood or recycled steel, or they could be materials that are particularly durable, reducing the need for replacement.
Importance of Green Building Materials
Now that we know what green building materials are, let’s talk about why they’re so important.
In a world where climate change and environmental sustainability are at the forefront of our minds, using green building materials is a powerful way to make a difference.
They help to reduce waste, cut energy consumption, and can even improve our health by creating better quality indoor environments.
Plus, they’re often more cost-effective in the long run.
So, whether you’re a builder, a homeowner, or just someone who cares about our planet, the importance of green building materials is clear.
They’re not just a trend, they’re the future of construction.
25 Green Building Materials List:
1. Bamboo: This fast-growing plant is a renewable resource that’s strong, durable, and versatile. It’s often used as a sustainable alternative to hardwood.
2. Recycled Steel: Steel is highly recyclable and using recycled steel can save significant amounts of energy compared to producing new steel.
3. Reclaimed Wood: This is wood that has been taken from old buildings and repurposed. It reduces the demand for new timber and adds a unique aesthetic to buildings.
4. Cork: This is a renewable resource harvested from the bark of cork oak trees. It’s used for insulation and flooring.
5. Straw Bales: Used in place of concrete, plaster, or wood, straw bales can provide good insulation.
6. Recycled Plastic: Plastic waste can be recycled and transformed into building materials like insulation and structural components.
7. Rammed Earth: This involves compacting a mixture of earth, sand, silt, and clay between forms to build walls.
8. Wool Insulation: Sheep’s wool is a natural insulator and can be used in place of synthetic insulation materials.
9. Denim Insulation: Yes, you read that right! Old denim can be recycled and turned into an effective insulation material. It’s safe to handle and has good thermal performance.
10. Recycled Fiberglass: Fiberglass is often used for insulation, and recycled fiberglass offers a more sustainable alternative to new production.
11. Solar Panels: While not a traditional building material, solar panels can be integrated into the design of a building to provide renewable energy.
12. Low-Emissivity (Low-E) Glass: This type of glass has a special coating to reflect infrared light, helping to keep heat inside in the winter and outside in the summer.
13. Hempcrete: Made from the woody core of the hemp plant mixed with lime, Hempcrete is a sustainable and efficient insulation material. It’s breathable, non-toxic, and has excellent thermal and acoustic performance.
14. Mycelium: This is a type of fungus that can be grown into specific forms, creating a natural and biodegradable building material.
15. Ferrock: This is a carbon-negative cement alternative made from waste steel dust and silica from ground-up glass.
16. Bio-glass: This is a type of glass made entirely from recycled glass, without any additional colorants or additives.
17. Recycled Metal: In addition to steel, other metals like aluminum and copper can also be recycled and used in construction.
18. Earth Bags: These are bags filled with earth that are stacked to form walls, similar to sandbags used in flood control.
19. Plant-based Polyurethane Rigid Foam: This is a type of insulation made from plants like bamboo, hemp, and kelp, offering high levels of thermal resistance.
20. Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs): These are high-performance building systems for residential and light commercial construction. The panels consist of an insulating foam core sandwiched between two structural facings, typically made of oriented strand board
21. Cool Roofs: These are roofs designed to reflect more sunlight and absorb less heat than a standard roof, reducing the need for air conditioning.
22. Low VOC Paint: Traditional paints can release harmful chemicals into the air. Low VOC (volatile organic compounds) paints improve indoor air quality.
23. Natural Clay: Clay is a natural material that can regulate humidity, resist fire, and provide thermal mass.
24. Papercrete: This is a material made from recycled paper. It’s lightweight, insulating, and can be used in a variety of applications.
25. Recycled Rubber: Old tires can be recycled into a variety of building materials, including roofing, flooring, and pavers.
These are just a few examples of the many green building materials available today. The best choice depends on the specifics of the project and the local environment.
Remember, the best green building material to use can depend on many factors, including the local climate, the type of building, and specific project goals.
Benefits of Green Building Materials
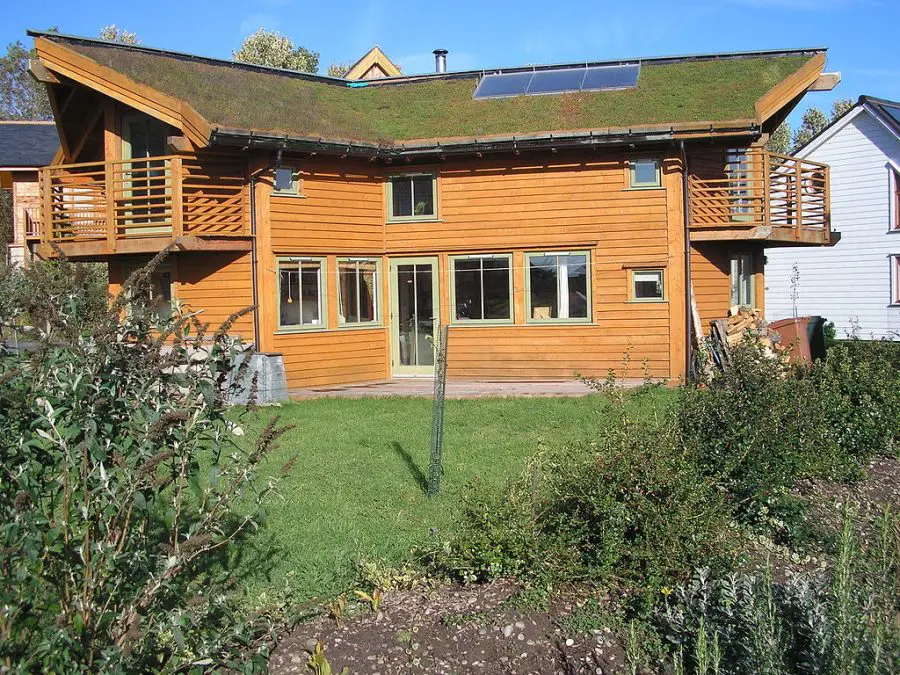

Are you ready to explore the world of green building materials? Let’s delve into the myriad benefits they offer.
From contributing to a healthier planet to providing economic advantages, green building materials are truly transformative.
They also play a significant role in enhancing our communities and promoting resource efficiency.
So, whether you’re an experienced builder, an aspiring architect, or simply an interested reader, come along as we navigate the remarkable benefits of green building materials.
You might be amazed at the substantial positive impact they can have!
Environmental Impact
Reduction in Energy Use: Green building materials often have excellent insulation properties, meaning they keep buildings warmer in winter and cooler in summer.
This reduces the need for artificial heating and cooling, leading to significant energy savings.
Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: By using less energy, we also reduce the amount of greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere.
Plus, many green building materials are produced in a way that emits fewer greenhouse gases compared to traditional materials.
Water Conservation: Some green building materials can help conserve water.
For example, green roofs can collect rainwater, reducing the need for irrigation.
Improved Air Quality: Many traditional building materials emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) which can harm indoor air quality.
Green building materials typically have low or zero VOC emissions, leading to healthier indoor air.
Economic Benefits
Lower Operating Costs: The energy savings from using green building materials can translate into lower energy bills, reducing the operating costs of a building.
Enhanced Asset Value and Profits: Buildings made with green materials can command higher prices and rent, enhancing their asset value. They can also attract tenants more easily, leading to higher occupancy rates and profits.
Optimized Life-cycle Economic Performance: Green building materials often last longer than traditional materials, reducing the need for replacement and maintenance.
Market Transformation: As demand for green building materials grows, it can stimulate the market, leading to more innovation and lower prices.
Health and Community Benefits
Improved Air, Thermal, and Acoustic Environments: Green building materials can contribute to a healthier and more comfortable indoor environment, with better air quality, temperature regulation, and noise reduction.
Enhanced Occupant Comfort and Health: Buildings made with green materials can be healthier and more comfortable to live in, leading to improved human health and wellbeing.
Minimized Strain on Local Infrastructure: By reducing the need for energy and water use, green buildings can reduce the strain on local infrastructure.
Improved Quality of Life: By contributing to a healthier environment and community, green building materials can help improve quality of life.
Material Efficiency
Durable Materials: Green building materials are often more durable than traditional materials, meaning they last longer and need to be replaced less frequently.
Locally Available: Using locally available materials can reduce the environmental impact of transportation and support the local economy.
Recycled Content: Materials with recycled content reduce the need for new raw materials and waste.
Reusable or Recyclable: Materials that can be reused or recycled at the end of their life reduce waste and can create a circular economy in the building industry.
Green Building Standards and Certification Systems

Ever heard of green building standards and certification systems? If not, you’re about to get a crash course!
These systems play a crucial role in the world of sustainable construction, setting the bar for what it truly means to be ‘green’.
They’re like a roadmap, guiding us towards more sustainable practices and ensuring that ‘green’ isn’t just a buzzword, but a reality.
In this section, we’ll be exploring some of the leading standards in the construction industry, including LEED and Green Globes.
So, whether you’re a professional in the field or just keen to learn more, let’s dive in and discover how these systems are shaping the future of green building!
LEED
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) is one of the most popular green building certification systems in the world.
Developed by the U.S. Green Building Council, LEED provides a framework for healthy, highly efficient, and cost-saving green buildings.
It covers aspects like water efficiency, energy costs and use, materials selection, indoor environmental quality, and more.
A building can achieve different levels of LEED certification, from Certified to Platinum, based on the number of points it earns across these categories.
So, when you see a building with a LEED plaque, you know it’s designed with sustainability in mind!
BREEAM
Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method (BREEAM) is another widely recognized green building certification.
Originating in the UK, BREEAM assesses the sustainability of buildings in a variety of categories, including energy, health and wellbeing, innovation, land use, materials, management, pollution, transport, waste, and water.
Like LEED, buildings can achieve different levels of BREEAM certification, from Pass to Outstanding.
BREEAM is all about promoting best practices in sustainable design and has been instrumental in driving the global green building movement.
Green Globes
Green Globes is a flexible and inclusive green building certification program used in the United States and Canada.
It offers a practical and affordable way to advance the overall environmental performance and sustainability of commercial buildings.
The system uses a questionnaire to assess a building in several areas, including energy, water, resources, emissions, and indoor environment.
One of the unique features of Green Globes is its interactive, online assessment process, which provides real-time feedback as users complete the questionnaire.
It’s a user-friendly system that’s helping to make green building more accessible.
Sustainable Building Materials FAQs
Now, let’s tackle some of the most frequently asked questions about green building materials.
We all have questions when diving into a new topic, right?
Whether you’re wondering what exactly green building materials are, why they’re important, or how they contribute to sustainability, we’ve got you covered.
This section is all about answering those burning questions you might have.
So, let’s get those gears turning and dive into the FAQs about green building materials.
Who knows, you might just find the answers to questions you didn’t even know you had!
Q. What are green building materials?
A. Green building materials, also known as sustainable building materials, are materials that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building’s life cycle.
This means they help to minimize the environmental impact of the construction and operation of buildings.
They can be made from renewable or recycled sources, and they often have properties that improve the energy efficiency or indoor air quality of a building.
Q. Why are green building materials important?
A. Green building materials are important for several reasons.
They help to reduce the environmental impact of building construction and operation, by saving energy, reducing carbon emissions, and minimizing waste.
They can also improve the health and comfort of building occupants, by improving indoor air quality and providing a healthier living environment.
Plus, in many cases, they can save money over the long term, through reduced energy and maintenance costs.
Q. What are some examples of green building materials?
A. There are many different types of green building materials.
Some examples include bamboo, which is a fast-growing and renewable resource; recycled steel, which saves energy compared to producing new steel; reclaimed wood, which reduces the demand for new timber; and low-emissivity (Low-E) glass, which can help to reduce energy use in buildings.
Other examples include recycled plastic, wool insulation, solar panels, and materials made from recycled content.
Q. How do green building materials contribute to sustainability?
A. Green building materials contribute to sustainability in several ways.
They help to reduce the environmental impact of buildings, by saving energy, reducing our carbon footprint along with lower carbon dioxide emissions, and minimizing waste.
They also contribute to social sustainability, by improving the health and comfort of building occupants.
And they can contribute to economic sustainability, by reducing the operating costs of buildings. In this way, green building materials can help to support the triple bottom line of sustainability: people, planet, and profit.
Advantages of Green Building Materials Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of green building materials, it’s time to reflect on what we’ve learned. It’s been quite a journey, hasn’t it?
We’ve delved into the environmental, economic, and health benefits of these sustainable superstars, answered some common questions, and even got to grips with green building standards.
But remember, this is just the beginning. The world of green building materials is vast and ever-evolving, and there’s always more to discover.
So, as we conclude, let’s look back at the highlights and look forward to a greener, more sustainable future in construction.
Ready? Let’s dive into the conclusion!
Recap of the Advantages of Green Building Materials
As we’ve journeyed through the world of green building materials, we’ve discovered a wealth of advantages that these sustainable alternatives bring to the table.
From their significant environmental impact, including energy reduction, lower greenhouse gas emissions, water conservation, and improved air quality, to their economic benefits, such as lower operating costs and enhanced asset value.
We’ve also seen how they contribute to healthier and more comfortable living and working environments, and how they promote efficient use of resources.
It’s clear that the advantages of green building materials are far-reaching and transformative.
Future of Green Building Materials
Looking ahead, the future of green building materials is bright and promising.
As awareness of environmental issues continues to grow, so does the demand for sustainable construction methods.
Innovations in technology and design are constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, leading to the development of new and even more efficient green building materials.
Furthermore, as more and more buildings seek green certification, the use of these materials is set to become the norm rather than the exception.
So, as we move forward, we can expect to see green building materials playing an increasingly important role in creating a sustainable and resilient built environment.