Are you ready to take a step further into sustainability? Extending zero waste principles and practices isn’t just about recycling more; it’s about rethinking how we use resources every day.
Join us as we delve into simple, impactful ways to minimize waste and maximize our environmental stewardship. Let’s make a sustainable impact together!
Key Takeaways:
- Zero Waste is a Lifestyle Change: Embracing zero waste means changing daily habits to reduce, reuse, recycle, and rot, aiming for a lifestyle with minimal environmental impact.
- Community Involvement is Crucial: Local composting programs, zero-waste events, and educational outreach are effective ways for communities to enhance sustainability efforts.
- Businesses Have a Significant Role: Companies can drastically reduce waste by adopting sustainable practices like eco-friendly packaging and product lifecycle responsibility.
- Education and Participation are Key: Understanding zero waste practices and actively participating in them helps individuals and communities make a significant positive impact.
- Small Actions Lead to Big Changes: Even simple actions like using reusable bags or participating in a local clean-up can reduce waste and conserve resources.
These points highlight the importance of collective and individual efforts in achieving zero waste goals and creating a sustainable future.
Introduction to Extending Zero Waste Principles and Practices

Imagine a world where nothing is wasted and where every item has a purpose and a place.
This is the vision of the zero waste movement. It’s not just about recycling more, but rethinking our entire approach to resources.
In this post, we’ll explore how to extend zero-waste principles beyond the basics, transforming our daily habits into powerful acts of environmental stewardship.
Join us as we dive deep into innovative practices that can make sustainability a part of every aspect of our lives.
Zero waste, or waste minimization, is a set of principles focused on waste prevention that encourages redesigning resource life cycles so that all products are repurposed (i.e. “up-cycled”) and/or reused. The goal of the movement is to avoid sending trash to landfills, incinerators, oceans, or any other part of the environment. Currently 9% of global plastic is recycled.[1] In a zero waste system, all materials are reused until the optimum level of consumption is reached. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zero_waste
What is Zero Waste?
Zero waste is a movement aiming to eliminate all trash from our lives.
It’s about reducing what we toss in landfills and changing how we view our resources.
Table for What is Zero Waste Management?
| Practice | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Refuse | Avoiding unnecessary products and packaging. | Reduces waste before it starts. |
| Reduce | Minimizing the amount of waste used. | Lowers overall waste production. |
| Reuse | Repurposing items multiple times before discarding. | Extends product life and reduces demand for new resources. |
| Recycle | Processing items to make new products. | Reduces demand for raw materials, and saves energy. |
| Rot | Composting organic waste to create soil amendment. | Enhances soil, and reduces landfill use. |
This table helps you to quickly grasp the key practices of zero waste management and their direct impacts on reducing waste.
What is Zero Waste?
Zero waste is not just a concept but a revolutionary way to look at our resources and waste systems.
It challenges us to change our lifestyles and communities to create a sustainable future.
Let’s break down what it means and how we can all contribute.
Zero Waste Explained: Definition and Overview of the Zero Waste Lifestyle
Zero waste is a sustainability philosophy that encourages the redesign of resource lifecycles so that all products are reused.
The goal is no trash sent to landfills, incinerators, or the ocean. It’s about making the most of our resources and minimizing our environmental impact.
Principles of Zero Waste: Foundational Principles Such as Waste Prevention, Reuse, and Recycling
The principles of zero waste revolve around waste prevention, reuse, and recycling.
These steps help us avoid unnecessary use of new materials, extend the life of products through reuse, and recycle what can’t be reused.
By adopting these principles, we aim to reduce our ecological footprint and promote a healthier planet.
What is Zero Waste Management?
Zero waste management is all about rethinking how we handle our trash. It’s not just throwing things away.
It’s about finding ways to make every item reusable, recyclable, or compostable.
Here’s how we can manage waste more effectively and keep it out of landfills.
Zero Waste Rules: Rules or Guidelines for Effectively Managing Waste
The rules of zero waste management focus on reduction first and diversion second. The key guidelines include:
- Refuse what you do not need.
- Reduce what you do use.
- Reuse what you consume.
- Recycle what you cannot refuse, reduce, or reuse.
- Rot (compost) the rest.
These steps help minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency, aiming to keep materials in use and out of the waste stream.
Zero Waste Pyramid: The Hierarchy in Zero Waste Management
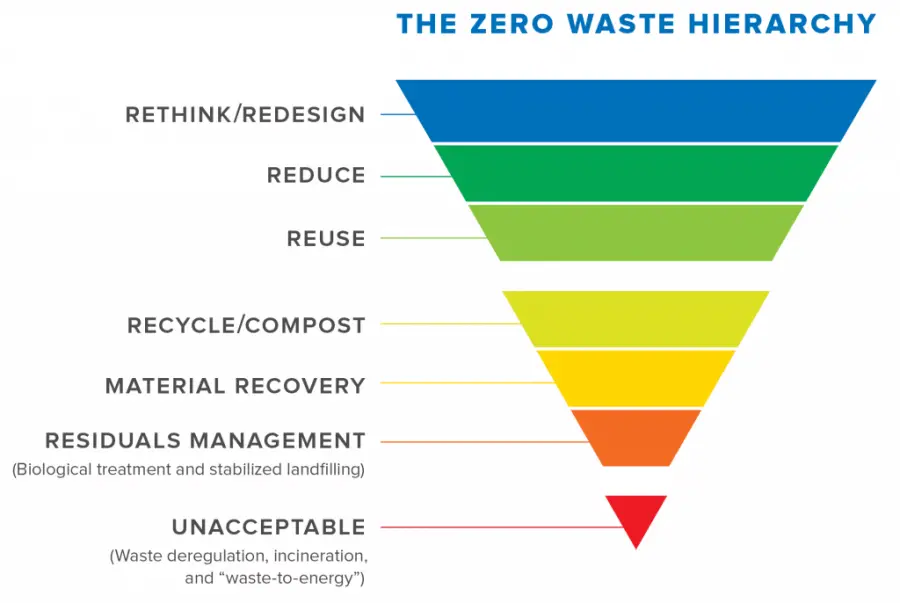
The zero waste pyramid is a visual guide that prioritizes waste management practices from most to least environmentally favorable:
- Prevention: Stopping waste before it starts by designing out waste and reducing excess.
- Reuse: Finding new uses for old items instead of disposing of them.
- Recycling/Composting: Processing used items into new products or composting organic waste.
- Energy Recovery: Recovering energy from waste that cannot be reused or recycled.
- Treatment/Disposal: The last resort for waste that cannot be processed through the above methods.
By following this hierarchy, we aim to minimize the environmental impact of our waste and turn what was once considered trash into valuable resources.
Zero Waste Examples – Zero Waste Lifestyle Tips

Individual Actions: Examples of Everyday Practices
Taking zero waste into our own hands starts with simple daily actions. Here are a few ways individuals can make a difference:
- Using Reusable Bags: Swap out single-use plastic bags for reusable ones during shopping.
- Composting Kitchen Waste: Turn your food scraps into nutrient-rich compost instead of sending them to the landfill.
- Choosing Refillable Products: Opt for refillable water bottles and coffee cups to minimize disposable waste.
These small changes, when adopted widely, can lead to significant reductions in waste.
Community Initiatives: Community-Led Programs
Zero Waste Strategies for Communities
Communities across the globe are taking up the challenge of zero waste through innovative programs:
- Local Composting Facilities: Many communities have set up composting centers that turn organic waste from homes and businesses into compost for local gardens and farms.
- Zero Waste Events: Events like farmers’ markets, festivals, and community gatherings often adopt zero waste policies, using reusable items and ensuring proper sorting of recyclables and compostables.
- Educational Workshops: Many communities offer workshops on recycling, composting, and reducing household waste to help residents learn how to live more sustainably.
These initiatives not only reduce waste but also strengthen community ties by bringing people together for a common cause.
Business Practices: Discussion on How Businesses Implement Zero Waste
Businesses play a crucial role in the zero waste movement by adopting sustainable practices:
- Sustainable Packaging: Companies are increasingly using materials that are either compostable or easy to recycle, reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills.
- Product Life-Cycle Responsibility: Some businesses take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their products, designing them to be easily disassembled and recycled or repurposed at the end of their useful life.
- Supporting Sustainable Suppliers: By choosing suppliers who also adhere to zero waste principles, businesses can ensure that their supply chain is sustainable from start to finish.
By integrating these practices, businesses not only minimize their environmental impact but also set a standard for others in their industry.
Table for Zero Waste Examples
| Action | Setting | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Using reusable bags | Individual | Reduces plastic waste, and lessens environmental impact. |
| Hosting zero-waste events | Community | Promotes sustainability, and educates the public on zero waste practices. |
| Implementing green procurement | Business | Reduces ecological footprint, and supports sustainable industries. |
This table showcases practical actions within various settings and outlines the benefits each action provides toward achieving zero waste goals.
Benefits of Zero Waste
5 Principles of Zero Waste: Detailed Benefits
Zero waste isn’t just good for the planet—it can also lead to significant benefits for individuals, communities, and economies.
Here’s how the five core principles contribute to these benefits:
- Refuse: By refusing unnecessary products and packaging, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce waste and save resources. This leads to lower production costs and less environmental depletion.
- Reduce: Reducing what we use and consume minimizes waste and conserves natural resources, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact. It also lessens the energy used in manufacturing, transporting, and disposing of goods.
- Reuse: Reusing items extends their life, decreases the demand for new products, and reduces the overall carbon footprint. Communities benefit from reduced waste management costs and less environmental pollution.
- Recycle: Recycling turns materials that would otherwise become waste into valuable resources, generating a new stream of materials and reducing the need to extract raw resources. This process also supports jobs in the recycling and manufacturing industries.
- Rot (Compost): Composting organic waste turns it into a resource, improving soil health and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers. This enhances food security and reduces greenhouse gas emissions from landfills.
Zero Waste Pros and Cons:
Zero waste practices offer numerous advantages, but there are also challenges to consider:
A Balanced View of the Advantages and Challenges of Implementing Zero Waste Practices
Pros:
- Environmental Impact: Significantly reduces landfill waste, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and conserves natural resources.
- Economic Benefits: Reduces costs associated with waste management and disposal, while promoting green jobs and industries.
- Community Health: Leads to cleaner air and water, which contribute to better health outcomes for community members.
Cons:
- Upfront Costs: Initial investments for zero waste infrastructure (like composting facilities) and sustainable product designs can be high.
- Convenience: Transitioning to zero waste requires changes in consumer behavior and may initially be less convenient than traditional waste systems.
- Accessibility: Access to zero waste options can be limited, particularly in under-resourced communities, which might not have easy access to recycling facilities or markets for sustainable products.
Understanding these pros and cons helps stakeholders make informed decisions about implementing zero-waste practices in their communities and businesses, aiming for a balance that maximizes benefits while addressing challenges.
Importance of Zero Waste Management
 Managing waste isn’t just about disposal—it’s about transforming how we view and handle resources.
Managing waste isn’t just about disposal—it’s about transforming how we view and handle resources.
Zero waste management is vital for sustainable living, impacting everything from local resources to global ecosystems.
Here’s how we can apply it beyond just our homes to really make a difference.
Expanding Zero Waste to Reduce Footprint
- Zero Based Principles: The Critical Role in Resource Conservation and Sustainability
- Emphasizes designing products and processes that minimize waste.
- Aims to protect natural resources and reduce environmental impacts.
- Extended Practices Beyond Home: Magnifying Positive Impacts in Various Settings
- In offices: Implementing digital solutions and recycling programs.
- During events: Using reusable materials and providing proper disposal options.
These steps help us reduce waste everywhere, making our world cleaner and more sustainable.
Importance of Zero Waste Management

Zero-Based Principles: The Critical Role of Zero Waste Management in Resource Conservation and Sustainability
Zero waste management is essential for both conserving our natural resources and achieving sustainability.
By embracing zero-based principles, we ensure that every product is designed with the end of its life in mind, promoting a circular economy where waste is minimized, and materials are kept in use.
This approach conserves resources and reduces pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, helping to mitigate climate change and preserve the planet for future generations.
Extended Practices Beyond Home:
How Zero Waste Principles Can Be Applied in Less Typical Environments
Extending zero waste principles beyond the home can significantly enhance their impact.
Advanced Zero Waste Techniques
In office settings, this might involve implementing digital document systems to reduce paper use or setting up dedicated bins for recycling and composting.
At public events, organizers can prioritize zero waste by providing reusable utensils and plates and by planning for proper waste sorting stations.
Zero Waste Management and Implementation
These practices reduce waste and set a visible example for others, spreading the zero waste philosophy and encouraging broader adoption.
By applying zero waste management in these varied environments, we create more sustainable communities and workplaces.
We demonstrate that zero waste can be integrated into every part of our lives.
Zero Waste Innovations
This widespread implementation not only magnifies the environmental benefits but also fosters a culture of sustainability that can lead to even more innovative solutions to waste reduction.
FAQs on Extending Zero Waste Principles and Practices

Diving deeper into zero waste helps our planet and also enriches our lives.
Let’s explore some common questions about how you can extend these principles into more areas of your life and community.
Q. What are some practical ways I can practice zero waste at home?
A. Start by focusing on the basics: refuse what you don’t need, reduce what you do need, reuse as much as possible, recycle right, and rot (compost) the rest.
Simple actions like using reusable containers, choosing package-free products, and starting a compost bin can make a big difference.
Q. How can my community get involved in zero waste initiatives?
A. Communities can support zero waste by establishing local composting facilities, organizing zero waste events, and conducting education and outreach programs to raise awareness.
Additionally, participating in community composting programs and supporting businesses that prioritize sustainability are great steps.
Q. What role can businesses play in promoting zero waste?
A. Businesses can significantly impact by adopting sustainable packaging, taking responsibility for the lifecycle of their products, and implementing green procurement policies.
Supporting businesses that practice product stewardship and choose eco-friendly materials is crucial for extending zero-waste practices.
Q. Can zero waste principles be applied in schools and workplaces?
A. Absolutely! Schools and workplaces can promote zero waste by reducing paper use, encouraging recycling and composting, and educating about sustainability.
Implementing programs like recycling bins in common areas and digital resources can greatly reduce waste.
Q. What are some innovative zero-waste practices that are less commonly known?
A. Beyond the usual practices, consider participating in fix-it clinics to repair items, joining zero-waste advocacy groups, and engaging in local zero-waste challenges.
These activities help instill a culture of resource conservation and inspire others to join the movement.
By understanding these FAQs and taking action, you can significantly contribute to a sustainable future, demonstrating that every small effort counts towards a larger goal of zero waste.
Conclusion: Extending Zero Waste Principles and Practices
As we wrap up our exploration of zero waste principles and practices, it’s clear that extending these into all areas of our lives is not just beneficial but necessary for a sustainable future.
Here’s a final nudge to make those eco-friendly changes:
Extending zero waste principles and practices involves reducing waste, reusing materials, and recycling effectively to minimize environmental impact.
It focuses on innovative ways to prevent waste creation, supports sustainable living, and promotes community-wide adoption of eco-friendly habits.
Recap of the Importance of Expanding Zero Waste Practices
- Zero waste is more than just a personal choice; it’s a community-wide commitment that benefits the environment, economy, and public health.
- By minimizing waste, we preserve natural resources and reduce pollution, ensuring a healthier planet for future generations.
Encouragement for Readers to Adopt Zero Waste Principles
- Every small step counts!
- Whether it’s choosing reusable over disposable, buying in bulk, or simply educating yourself and others about sustainable practices, your actions make a difference.
- Embrace zero waste habits at home, work, and in your community.
Call to Action for Community Involvement and Personal Responsibility in Waste Reduction
- Get involved and lead by example! Support local zero waste initiatives, participate in community clean-ups, and advocate for policies that encourage sustainable practices.
- Your involvement not only contributes to a cleaner environment but also inspires others to take action.
Together, let’s commit to these principles, making zero waste a way of life that extends beyond our homes to touch every part of our community.
Read our article and learn more: Mastering Zero-Waste Living: 7 Easy Tips and Tricks
Resource Section
Exploring zero waste principles further can help you make significant changes in your lifestyle and community.
Here are some authoritative resources that provide comprehensive information, practical tips, and global perspectives on zero waste:
Zero Waste International Alliance (ZWIA):
A global organization dedicated to advancing zero waste policies and practices worldwide. It offers a wealth of resources, including guidelines and standards for communities and businesses aiming to achieve zero waste. Visit ZWIA
Zero Waste USA:
A leading resource for zero waste tools and information in the United States, offering training, certification programs, and local chapter information to help individuals and communities increase their waste diversion rates. Visit Zero Waste USA
EarthEasy:
Provides practical environmental tips and products for sustainable living. Their guide on zero waste offers easy steps to reduce waste in everyday life. Visit EarthEasy
The Story of Stuff Project:
A platform that produces documentaries and offers educational content on the impact of consumer culture on the environment, focusing on ways to transition to a zero-waste lifestyle. Visit The Story of Stuff Project
Sustainably Forward:
This site offers insightful articles on a wide range of zero-waste topics, from beginner tips to in-depth discussions on waste management systems. Visit Sustainably Forward
These resources can provide the knowledge and inspiration needed to deepen your commitment to zero waste practices, helping you and your community move towards a more sustainable future.







